sep . 24, 2024 12:00 Terug naar lijst
The composition and working principle of the camera module
The composition and working principle of the camera module
1. The composition of the camera
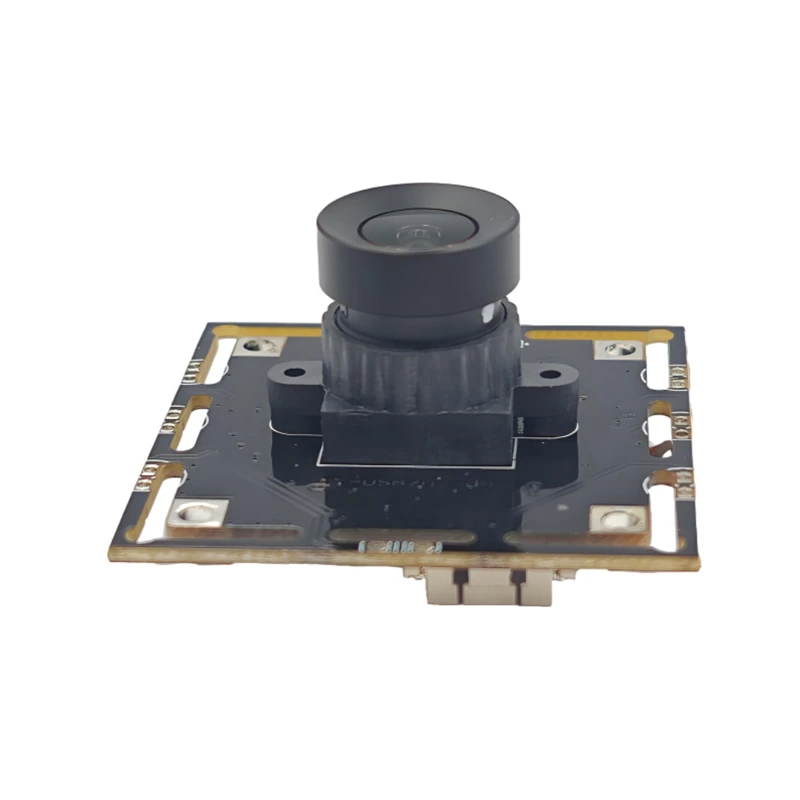
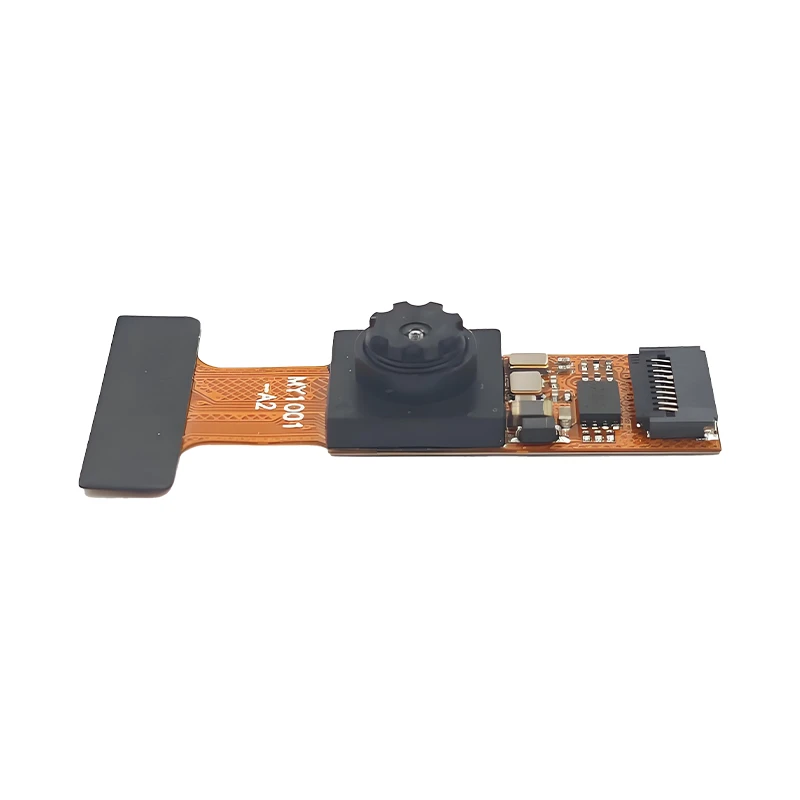
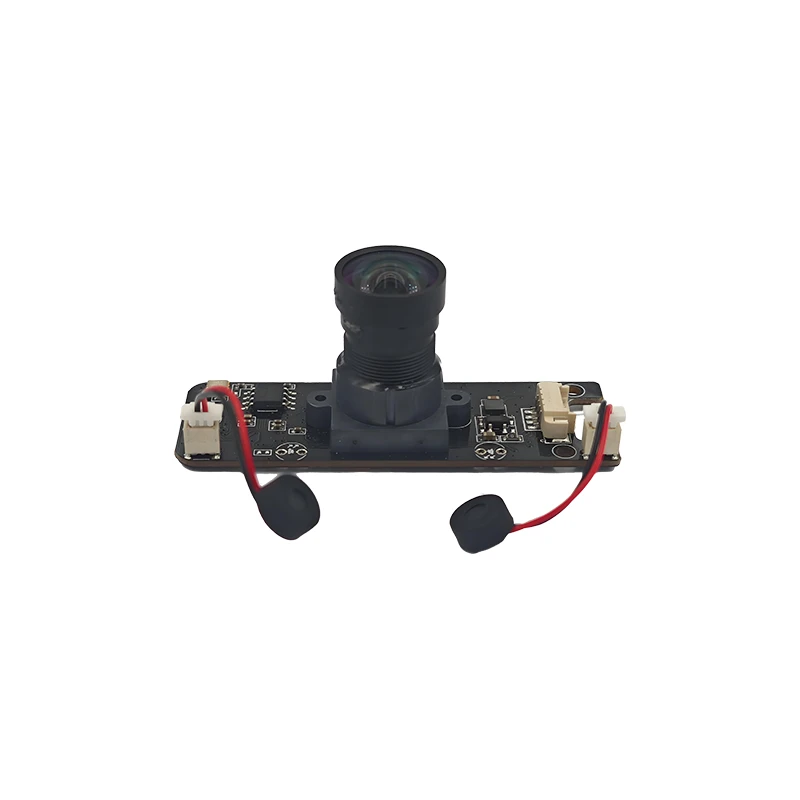
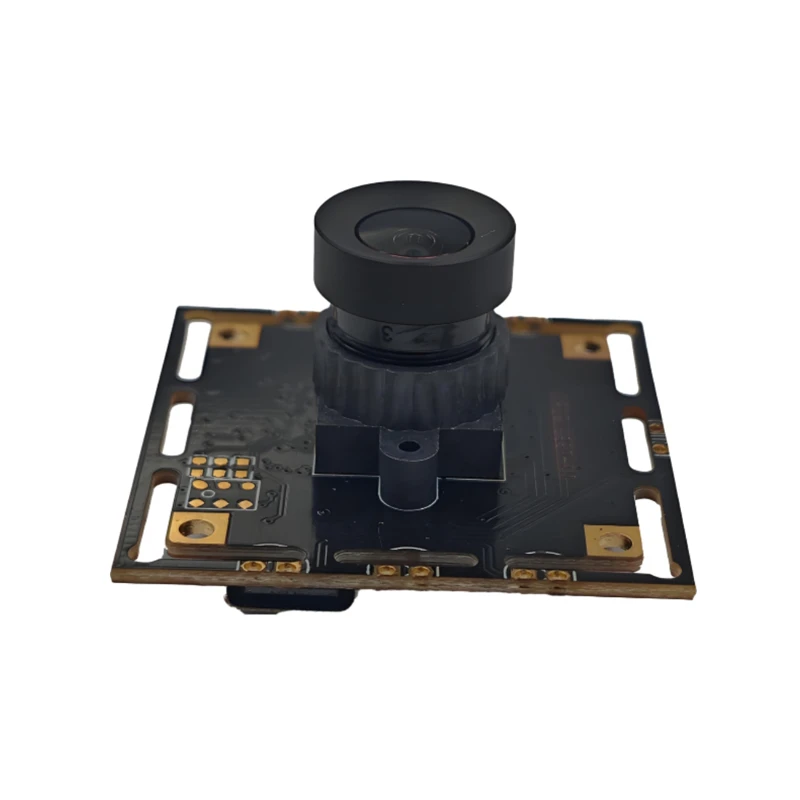
The four main parts of the camera are the photosensitive chip (CMOS), the decoding chip (also called the digital signal processor DSP), the lens, and the PCB/FPC

2. Working principle: The reflected light of the object is gathered by the lens (lens), and the light signal is converted into an electrical signal through the CMOS or CCD integrated circuit, and then converted into a digital image signal through the internal image processor (ISP) and output to the digital signal processor (DSP) for processing, and converted into a standard MJPEG, YUV and other format image signal.
The lens (lens) is the soul of the camera. The lens (lens) has a very important effect on the imaging effect. It uses the refraction principle of the lens. The scene light passes through the lens and forms a clear image on the focusing plane. The image of the scene is recorded through the photosensitive material CMOS or CCD sensor. Now the lens manufacturers have mainly turned to domestic production. The industry with high optical technology content such as lenses has a relatively high threshold. Well-known companies in the industry include Fuji Seiki, Konica Minolta, Largan, Enplas, etc.
Sensor is the core module of CCM. There are two types of sensors widely used at present: one is the widely used CCD (charge coupled device) element; the other is CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) device.
Charge coupled device image sensor CCD (charge coupled device) is made of a highly sensitive semiconductor material, which can convert light into electric charge and convert it into digital signals through analog-to-digital converter chips. CCD is composed of many photosensitive units, usually in units of millions of pixels. When the surface of CCD is illuminated by light, each photosensitive unit will reflect the charge on the component, and the signals generated by all photosensitive units are added together to form a complete picture. CCD sensors have a complex manufacturing process, which has led to the cost not being reduced.
Complementary oxide metal semiconductor CMOS (complementary l-oxide semiconductor) is mainly a semiconductor made of two elements, silicon and germanium, so that semiconductors with n (with - charge) and p (with + charge) levels coexist on CMOS. The current generated by these two complementary effects can be recorded and read into images by the processing chip.
The image processing chip (DSP) is an important part of CCM. Its function is to transmit the data obtained by the photosensitive chip to the central processor in a timely and fast manner and refresh the photosensitive chip. Therefore, the quality of the DSP chip directly affects the image quality (such as color saturation, clarity, etc.)
-
Say some things about usb camera modules (usb camera PCBA)
NieuwsFeb.22,2025
-
Wide dynamic range AI usb camera modules
NieuwsOct.28,2024
-
Windows hello face recognition binocular usb camera
NieuwsOct.21,2024
-
Do you like this cute design usb AI camera?
NieuwsSep.24,2024
-
AI and increasingly advanced USB camera module technology make people's lives more convenient
NieuwsSep.24,2024